Introduction
Gallium is a chemical element with symbol Ga and atomic number 31.

History
In 1871 the existence of gallium was first predicted by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, who named it "eka-aluminium" from its position in his periodic table.

In 1875 was found in spectroscopic discovered by French chemist Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran and lecoq succeeded in obtaining gallium pure by electrolysis gallium hydroxide (Ga(OH)³).

Properties of Gallium
Physical Properties:

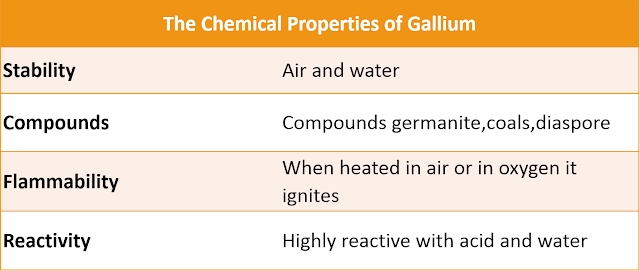
Chemical Properties:
Source
Gallium is not found in the form elements on the Earth, but is found in minerals and ores in the Earth's crust.
Diaspora (α-AlO(OH))

Coal (C₁₃₇H₉₇O₉NS)

Coal (C₁₃₇H₉₇O₉NS)

Sphalerite (Zn, Fe)S

How get the pure Gallium
Ga
Ga (OH)₃ + 3 H⁺ → Ga³⁺ + 3 H₂O
Ga (OH)₃ + OH⁻ → Ga(OH)₄⁻
Applications


The uniques of Gallium


Gallium is a chemical element with symbol Ga and atomic number 31.

In 1871 the existence of gallium was first predicted by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, who named it "eka-aluminium" from its position in his periodic table.


Physical Properties:


Gallium is not found in the form elements on the Earth, but is found in minerals and ores in the Earth's crust.
Diaspora (α-AlO(OH))




- Pure gallium metal by electrolysis current through a gallium compound, such as gallium oxide (Ga₂O₃).
- Commercially, most gallium is extracted as a by product of aluminum and zinc production.
- Gallium is also extracted from the flue dusts of coal.
Ga
- N: Gallium nitride
- Cl₂: Gallium (II) chloride
- O: Gallium oxide
- Br₃: Gallium tribromide
- F₃: Gallium trifluoride
- S: Gallium sulphide
- The reaction of gallium with acid
Ga (OH)₃ + 3 H⁺ → Ga³⁺ + 3 H₂O
- The reaction of gallium with base
Ga (OH)₃ + OH⁻ → Ga(OH)₄⁻
- The reaction of gallium with halogen
Applications
- Gallium as minerals and vitamins in the human body
- Gallium arsenide is used to make laser diodes that produce light from electricity
- Gallium is used to create an LED a bright blue
- Create brilliant mirrors
- As the mixture for nuclear weaponse
- Gallium-67 used for tumor imaging and localisation of inflammatory lesions (infections)
- Gallium-68 positron emitter used in PET and PET-CT unit derived from germanium-68 in the generator.


- Gallium is also dubbed as the "heart beat“
- Gallium can melts in the hand
- Gallium can soften and destroy the structure of the cans
- Gallium is capable of attacking other metals, Example: Aluminum


References
- W. M. Haynes, ed., CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, 95th Edition, Internet Version 2015, accessed December 2014.
- John Emsley, Nature’s Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements, Oxford University Press, New York, 2nd Edition, 2011.
- Boca Raton, FL, 95th Edition, Internet Version 2015, accessed December 2014. Tables of Physical & Chemical Constants, Kaye & Laby Online, 16th edition, 1995. Version 1.0
- T. L. Cottrell, The Strengths of Chemical Bonds, Butterworth, London, 1954.
- Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility - Office of Science Education, It’s Elemental - The Periodic Table of Elements, accessed December 2014.
Baca Juga :